
Feels like peak Gould. This May 1944 Sunday shows off Gould’s visual sense of place, love of clean geometry and perspective, retributive Justice.

Feels like peak Gould. This May 1944 Sunday shows off Gould’s visual sense of place, love of clean geometry and perspective, retributive Justice.


Even 30 years into one of the most successful runs in comic strip history, Chester Gould’s Dick Tracy continued to promote itself to new newspapers that still hadn’t syndicated the iconic hero. This ad ran in Editor & Publisher, the longtime trade bible for print periodical publications. Of course, this “man of stature” led the most grisly, violent and truly weird of all American comic strips. It was also one of the most compelling. For a gallery of gruesome villain deaths, see this earlier post. On the impaling of The Brow. On the general strangeness of Gould’s imagination. On Gould and Tracy’s conservatism.

Retribution was Chester Gould and Dick Tracy’s model for justice from the beginning. The strip started in 1931 literally as a revenge narrative. Standing over the murdered body of his fiancé Tess Trueheart’s father, civilian Tracy swears vengeance on the killers. He quickly joins the police force, but the themes of retribution and conviction by poetic justice remained a hallmark of the strip across four and a half decade run. From the beginning Chester Gould unapologetically crossed the lines of good taste. By the late 1930s in criminals like The Mole, B.B. Eyes, Flattop, Pruneface and the like, Gould started using outward disfigurement as expressive of inner villainy. And the level of explicit violence and even torture in Dick Tracy was unlike anything else on the comics page, or elsewhere in pop culture for that matter.
The revenge motif was baked into the strip’s moral universe. Tracy villains didn’t just need to be sought, caught and jailed. They needed to be hounded and often tortured along the way. Many of Tracy’s prey ended up behind bars, but just as often they met poetically just ends. Gould turned the grisly, fitting deaths of villains into his own special kind of art. Here are some examples from the first two decades of the strip that highlight Gould’s dark talent for retributive justice and capital punishment Dick Tracy style. At these climactic moments we see most clearly the visual, moral and often bizarre world,
Subtlety was not in Chester Gould’s quiver. Here he triple underlines his irony.
More than anything, Gould loved to kill and humiliate Tracy villains in slo-mo. Here, B-B Eyes hides in a garbage barge in the final leg of a desperate flight from justice, only to get dumped, trapped and drowned. Gould had a special talent for using the panel. framing and zoom techniques to communicate feeling through his use of space. His signature tight shots on dead villains often conveyed the loneliness and claustrophobia of death itself.

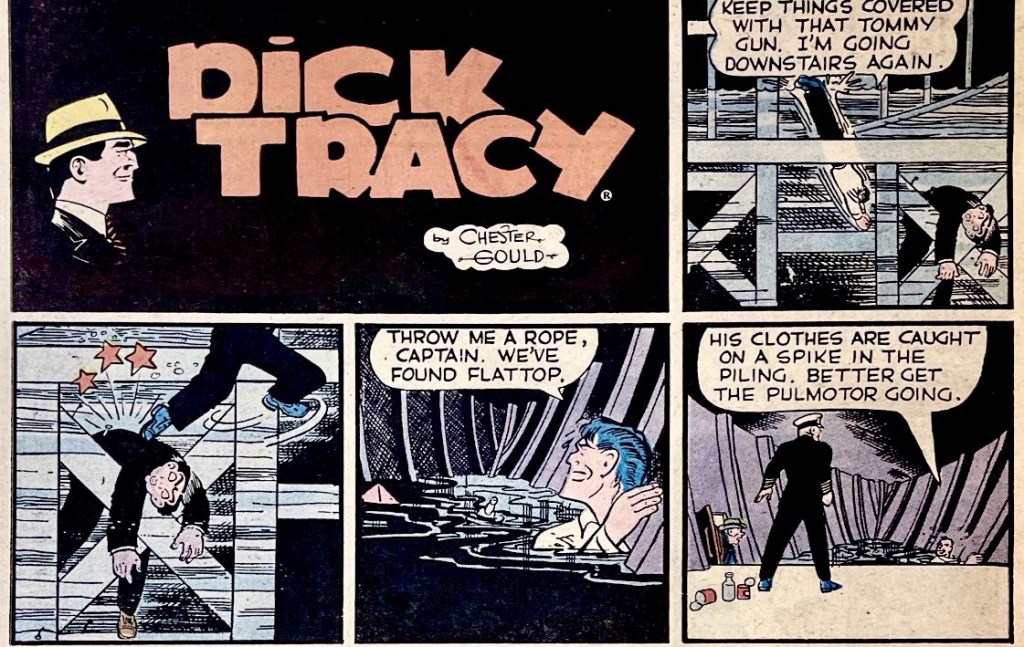
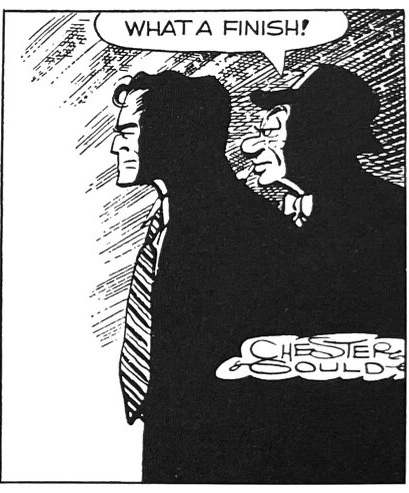
In 1944, Gould concocted two of his most venal villains. Flattop was simply psychopathic as a hit man, and he would be followed by The Brow, who was sadistic and a spy. Hiding beneath a ship being constructed, Flattop gets hung up on protruding spikes, leading to another close-up of deserving death.

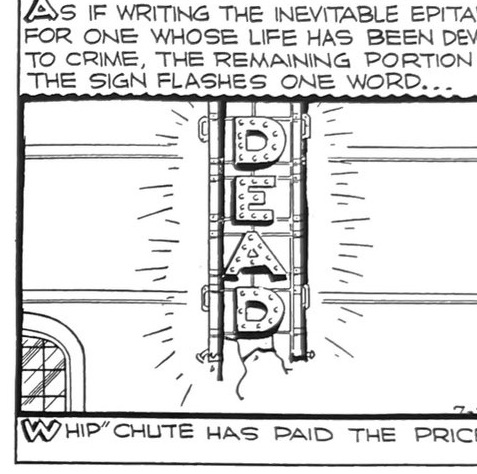
Far and away the most inventive and stomach-turning death in the first decades of Dick Tracy was the impaling of The Brow. I covered this in greater detail and with more context elsewhere. But here again is the wartime spy getting impaled on the flagpole commemorating the city’s war dead. The bending flagpole is a gruesomely brilliant touch to amplify that moment of maximal tension that will ultimately pierce the villain.
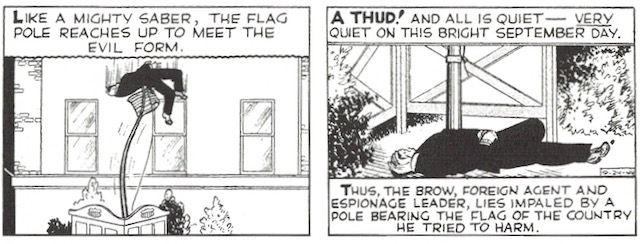
Falling through a skylight, again in comic strip slo-mo, Gargles gets sliced across three panels. And Gould can’t resist giving us his final shudders. In fact Gargles hangs on until the next strip so his final words exonerate an innocent suspect just in time for Christmas. One of the hallmarks of Dick Tracy was the strip’s extremism, Gould’s penchant for balancing unmatched graphic violence and angry vindictiveness with maudlin sentimentality. This sequence leads up to a Christmas strip that celebrates the villain’s death and the joy of the season.

Making a speech impediment somehow expressive of a villain’s evil was a questionable move to begin with. But Gould doubles down on this conceit by having Mumbles frantically, futiley hail for “ELP”.
Gould loved to draw in that little bit of grisly business to convey violence. While he used a heavy, cartoonish line and unreal, expressionist style that set the strip far apart from the illustrative style of most adventure strips, Gould used other ways of communicating hard-boiled reality. He had a penchant for objects penetrating bodies. Bullets often passed through their targets in shootout sequences. And as the deaths of The Brow and Gargles showed, the impaled body has a special place in Gould’s sense of horror. The death of T.V. Wiggles comes from fallen metal sheets that form an ersatz coffin. But it is that little corner of metal piercing a flap of neck flesh that telegraphs the experience of death itself.

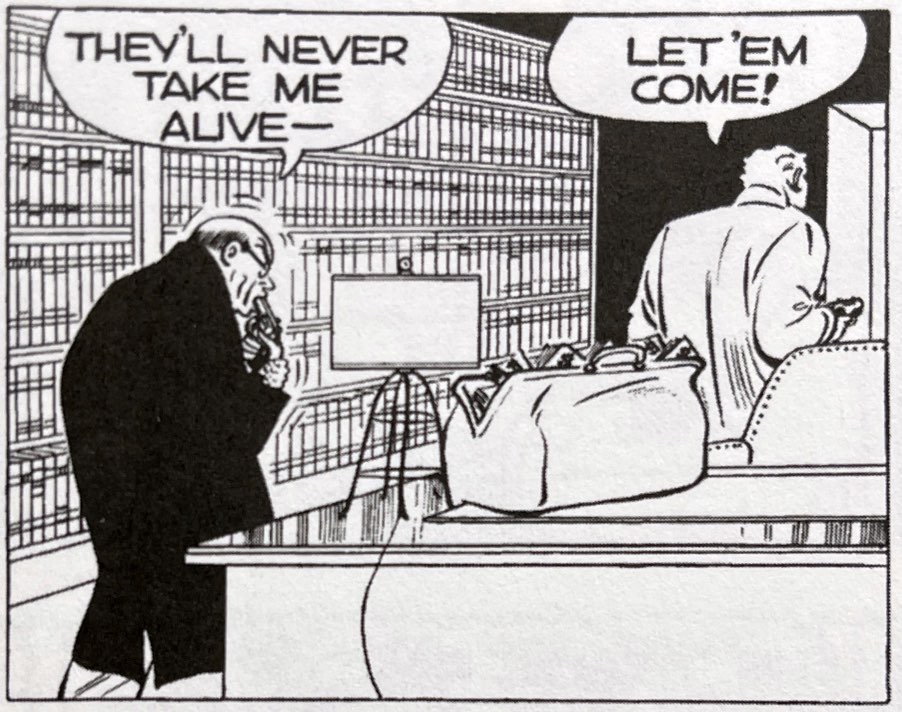
Mr. Crime was among Tracy’s most ruthless, pitiless villains of the 50s, and in the context of the Gould moral universe I am surprised (and a bit disappointed) that he suffers a simple shootout with Tracy. In fact Gould reserves the grisliest image for Mr. Crime’s extorted dupe, Judge Ruling. When cornered, the corrupt Judge chooses suicide. But of course Gould can’t give us a gunshot sound effect heard through a closed door. We have to get an image of Judge Ruling eating the gun, complete with cheek lines to suggest how deep he has planted the barrel. But we’re not done with this duo. As is his wont, Gould closes in for a final tableaux of both villains swimming in their own blood and money.

Flattop Jr. was indeed the son of the original Flattop, but he was framed by Gould as a neglected youth who embodied the overhyped scourge of the 1950s – the juvenile delinquent. He appears to meet his end in a theater fire he himself set to cover his escape. Despite the massive explosion Gould depicts dramatically, and the presumption of having died in the inferno, Jr. turns up later where his genuine death takes place in the middle of another villain’s cycle. And so that final contemplative panel here turns out to be ironic.

The hawklike nose and chin that stepped right off of Mount Rushmore were Dick Tracy’s visual signature. He was unapologetically a “square” literally inside and out. That rocklike defense of authority and institutions was precisely what Chester Gould intended as a counterpoint to the romanticized gangsterism of late Prohibition. And this impatience with “bleeding hearts” who seemed soft on crime was part of the strip from the start and an honest expression of Gould’s own sensibilities.
Tracy showed little regard for penal reform, rights of the accused or any ambivalence about police authority. Far from an aging curmudgeon, however, Gould’s views were present from the beginning of the strip and formed the center of the Dick Tracy ethos.
And so it should come as no surprise that from the start Tracy was not exactly a feminist treat. This early passage from the first year of Tracy around 1932 finds Dick being a real dick – mistakenly accusing his fiancé Tess Trueheart of ruining a planned raid on a gangster boss meeting by leaking the plan to friends. It’s a good example of Tracy as buffoon.


By the time Gould retired in the late 1970s Tracy had already become a counter-culture icon of right-wing deference to authority and defense of police at all costs. And this was nothing new. As early as the 1940s, rival cartoonist Al “Li’l Abner” Capp lampooned Tracy’s stoicism, violence and straitlaced devotion to law and order with his recurring Fearless Fosdick character.

Chester Gould’s imagination was as relentless as it was strange and even strangely mundane. His four decade run of Dick Tracy was distinguished by his signature villain grotesques, striking graphic violence and often arch-conservative politics. Reviewing Tracy’s first year of strips lately, I was struck by a few scenes that both veered from the strip’s eventual form but also practiced many of its regular notes. In the image above, for instance, Tracy pumps himself up for the coming challenge of bringing down his first major nemesis, Big Boy, and rescuing a kidnapped boy. The later Tracy would of course become a rock of resolve that wouldn’t have admitted even this kind of self-encouragement. At this point, even for Gould, Tracy is still human and not yet iconic.
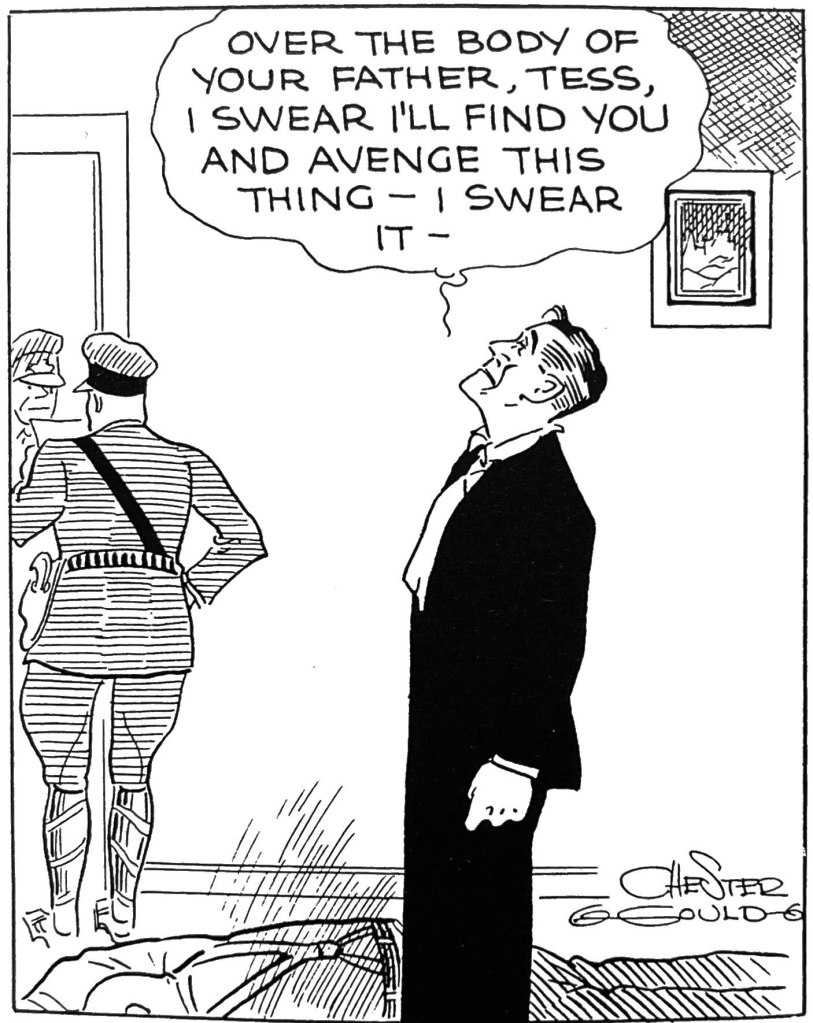
And yet the two-fisted and eccentric manliness of Tracy and many of his pulp fiction counterparts was central to the character from the beginning. And Gould’s politics clearly were already set as early as 1932. Tracy was conceived as a lawman who necessarily had one foot outside police institutions. In fact, before the murder of fiancee Tess Trueheart’s father Emil, Dick was a civilian who had not yet found his calling. He swears upon Emil’s dead body that he will avenge the murder, which sets him on a quick path to becoming a leader among the “plainclothes” unit of the city police department. But his impatience with the bureaucracy is apparent in his unconventional methods and capacity for personal revenge and violence upon his villains. When he finally corners Big Boy, we get a crescendo of police brutality that stretches across several days. It ends with Tracy sending Big Boy crashing through a ships’ cabin door.

The twisted genius of Gould was in having it both ways with Tracy. He professed a deep respect for the law, and Tracy’s straight-backed uprightness was a feature of the strip’s characterization as well as it’s blocky noir style. And yet vigilante justice was meted out both by Tracy and Gould alike. Indeed, his colleagues in the force like Pat Patton and subsequent colleagues are seen as relatively timid and even feminized by their institution in a way that the indomitable masculinity of Dick is not. And the overall violence of the strip is clearly an extension of Tracy’s own vengefulness. The protracted chase of villains on the lam became a part of the Dick Tracy formula, and it was punctuated by the villain’s gruesome torture by nature along the way, often ending in grisly death. Violence for Gould always seemed to be the ultimate social purifier.
By Gould’s own admission, he often made it up as he went along, rarely knowing where his plots were headed and how he would get Tracy out of a jam. And so from its early days the plotting and devices often feel ham-handed, implausible or genuinely weird. His pursuit of Big Boy onto an ocean liner leads Tracy to knock out an innocent staffer to don his uniform and to dress in drag just to get onto the boat and get close to the kidnappers. Less tortured paths clearly are available to his characters, but Gould’s love of novel, unlikely story paths usually wins out.

By 1942, a decade after its launch, Gould’s visual signature for Tracy is fully established. His hawklike nose, perpendicular chin and straight lips are as much a statue as a figure, more chiseled from stone than drawn in ink. And in this self-portrait Gould himself sweats under Tracy’s command. He has created a caricature of law and order, authority and masculinity that would become a lodestone. Al Capp soon would mock his violence and surreal story and villainy. His love of authority and violence, impatience with countercultural trends would make him seem a relic by the end of the run. Yet, as much as Gould himself seemed a straight arrow defender of formal institutions, Dick Tracy itself was grounded in a surreal imagination that eschewed simple realism, broke violently with the propriety of the comics page and took us into very strange places.


Nearly 25 years ago IDW’s Library of American Comics began reprinting the full run of Chester Gould’s Dick Tracy, starting with the strip’s premiere in late 1931. This week, with the release of Volume 29, the series reached its end, marking Gould’s retirement in 1977. I had been planning to mark this occasion by posting the very first 1931 strips alongside the very last 1977 strips to illustrate the evolution of Gould’s style as well as the decade’s long consistency of his vision. Little did I know that Gould himself would beat me to it. See below.

The first week or so of Tracy locates the origin of Dick’s moral commitment to fighting gangsters in the robbery/murder of Emil Trueheart, father of his new fiancé Tess. Tracy was not a cop by trade, but a young man still finding his way. In the sort of surrealistic moment that would typify Gould’s storytelling and visual style for the next 4 decades, Tracy not only finds his moral mission but becomes a “plainclothes” detective as well as a natural leader for the force within weeks of the strip’s launch. The moment of moral truth is captured in the featured panel at the top of this post.

Between 1931 and 1977 Gould’s style had gove through several evolutionary stages. By 1977, Gould’s ink lines had grown thicker and a bit rounder. His more extensive use of close-ups and medium frames were a begrudging accommodation to the shrinking space allotted to strip artists even by the late 1970s.
Gould invented his hero as “Plainclothes Tracy” in a series of spec strips he sent to legendary publisher Joseph Patterson, who was in the process of building the New York Daily News into a pioneer of tabloid newspapers. Patterson suggested the change of name to the simpler “Dick Tracy” and seemed to understand that Gould’s penchant for violence, grotesque villainy and even sadism mapped well against his vision of the tabloid style. The gorgeously colored Tracy Sunday strip would be the cover wrapper for the Sunday Daily News for decades.
Famous for the brutality of his cartoon vision of crime and punishment, it is revealing that the first panel of the Plainclothes Tracy spec strip is a scene of bondage and torture among thugs.


By the mid 1930s, his signature thick outlines, highly abstracted iconography, extensive use of fields of blacks, and series of bizarre villains were all fully established. The Sunday page below is from 1937 and The Blank adventure.

Dick Tracy holds a special place in my own journey into comic strips. The lush reprint of classic adventures, The Celebrated Cases of Dick Tracy by Bonanza Books in 1970 was one of a trio of reprints that captivated me with the form. It was around that time that I first got hold of Jules Feiffer’s The Great Comic Book Heroes and a Chelsea House oversized reprint of early Buck Rogers strips.
But it was Gould’s starkness in style and story, the extremity of art and character, that pulled me in then and still does decades later. I can think of no other comic strip artist that had such a singular vision. There has always been a peculiar geometry to Gould’s art. His panels alternated between use of deep perspective and no perspective, a weird penchant for flatness and depth. The stances of his characters, especially Tracy and his long inky black columnar legs, was so eccentric and physically improbable. Even though Gould became famous for his love of procedural detail in detection, gadgetry and eventually sci-fi crime-fighting inventions (i.e. the two-way wrist radio), his visual language was minimalist and abstract. His daily strip truly popped from the page of his fellow and able artists because it felt like being dropped into an expressionist daydream.
Gould was as famous for the brutal simplicity of his moral vision as he was for the violence of the action in his strips. The villains were not only surreal grotesques, but they met their end in grisly ways that suggested nature (or God) itself was meting final judgment. The impaling of wartime spy The Brow on an American war memorial flagpole is the best known. But Gould followed a formula with every adventure that moved towards a protracted manhunt and chase of the villain, which usually ended with the rogue’s end often via some strange knot of fate and chance.

Gould himself met a more peaceful end in 1985. The strip’s writer Max Collins and artist (ands former Gould assistant) Dick Locher memorialized him in the same simple, declarative style for which the master himself was known for decades.
